What is the Thin Film Deposition Technology? A Comprehensive Overview of Thin Film Deposition
Thin film deposition technology plays an important role in modern technology,
from cell phone screens to solar cells, everything relies on the use of
high-performance thin films.
As a professional manufacturer of thin film deposition equipment, Brother Furnace is committed to providing advanced thin film deposition solutions.
This article will comprehensively introduce the principles, applications, and related equipment of thin film deposition technology, aiming to reveal the deep value of this technology for you, and hopefully help you in your experiments or production.
What is Thin Film Deposition
Thin film deposition is the process of depositing specific materials onto the surface of a substrate in extremely thin layers, typically in the nanometer to micron range. These thin films can be a variety of substances, including metals, insulators, and semiconductor materials. Thin film deposition technology has a wide range of applications in many fields, especially in semiconductor manufacturing and optoelectronic devices.
Principles of Thin Film Deposition
The basic principles of thin film deposition techniques can be divided into
two main categories: chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and physical vapor
deposition (PVD). These two main techniques are described in detail below.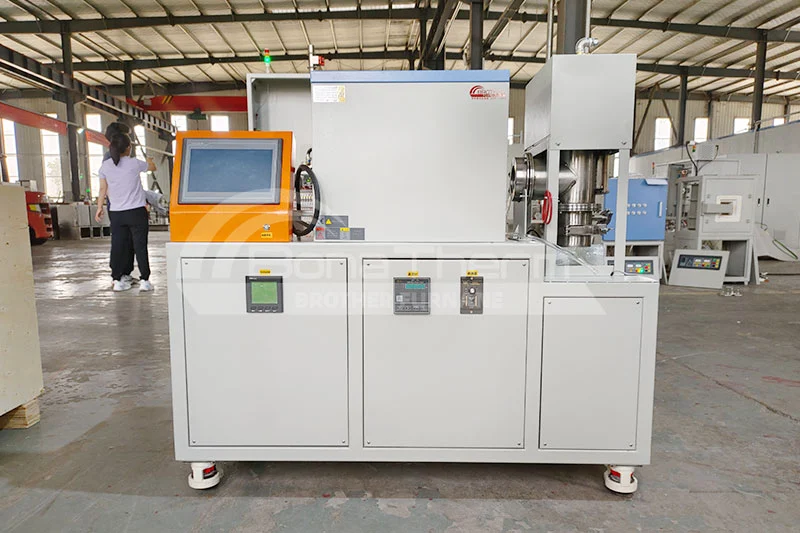
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
Principle: Vapor phase deposition is the process of converting a gaseous precursor into a solid film through a chemical reaction. The process is usually carried out in a high-temperature environment where the gas precursor reacts on the surface of the substrate to form a compound film.
Reaction conditions: Deposition rates and film quality are affected by several factors, including temperature, pressure, gas composition and flow rate. Different reaction conditions can affect the crystal structure, thickness, and uniformity of the film.
Advantages
1. It is possible to deposit uniform films on complex-shaped substrates.
2. The chemical composition and structure of the film can be regulated by selecting different precursors.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
Principle: Physical vapor deposition technology deposits material onto a
substrate through a physical process (e.g., evaporation, sputtering, etc.).
Unlike CVD, PVD is usually performed at relatively low temperatures.
Evaporation deposition: The material is heated to an evaporated state and the vapor is cooled and deposited on the substrate to form a thin film.
Sputtering deposition: The target material is bombarded by energetic particles, causing target atoms to escape and be deposited onto the substrate.
Advantages
1. High purity of the film, suitable for applications with strict requirements on film quality.
2. Wide range of applications, capable of depositing a wide range of materials.
Application of Thin Film Deposition Technology
Thin film deposition technology has a wide range of applications in several high-tech fields.
Semiconductor Industry
Application: In semiconductor devices, thin-film deposition is used to manufacture all kinds of circuits, sensors, and power devices. High-quality thin films can significantly improve the performance and reliability of devices.
Example: Silicon oxide and silicon nitride films are commonly used as
insulating and protective layers in chip manufacturing processes.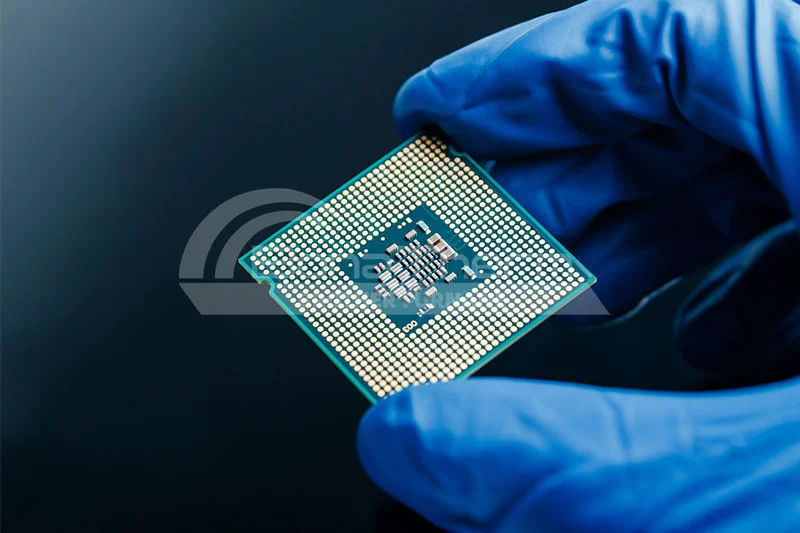
Optoelectronic Devices
Application: Thin-film deposition technology is critical in photovoltaic devices, especially in the manufacture of photovoltaic cells. By depositing highly efficient optical thin films, the energy conversion efficiency can be significantly improved.
Example: Polysilicon films deposited using CVD technology are the core material for modern solar cells.
Surface Protection
Application: Thin-film deposition technology enables the deposition of wear- and corrosion-resistant protective films on tools and machine parts, thus extending the service life of the product.
Example: Titanium Nitride films (TiN) are widely used to coat cutting tools to improve their wear resistance.
Optical Devices
Application: Thin film deposition technology is used in the manufacture of optical lenses, displays, etc. to help improve optical performance.
Example: Anti-reflection coatings and filters are realized by CVD and PVD technologies to improve light transmission and image quality.
Medical Devices
Application: In medical devices, thin-film technology is used to create biocompatible materials to improve the performance of implants.
Example: Bioceramic films deposited with CVD are used in orthopedic implants
to promote bone growth.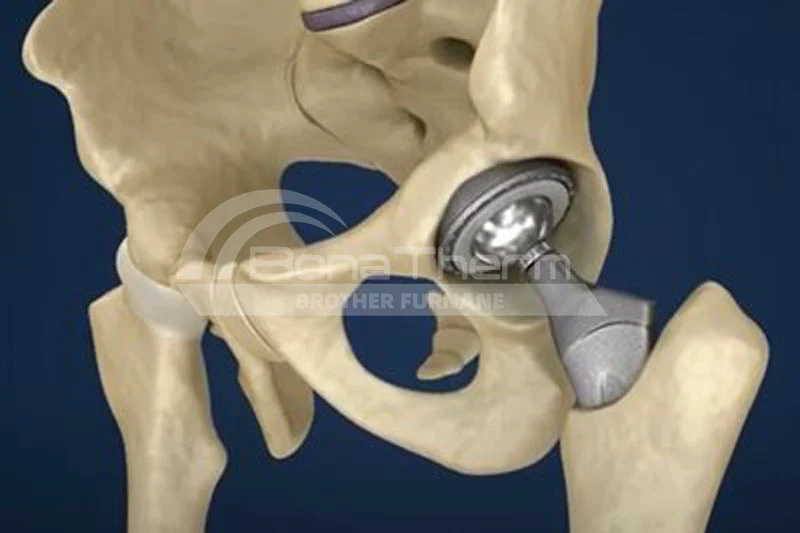
How to Choose the Right Thin Film Deposition Equipment
Choosing the right thin film deposition equipment is critical to ensuring productivity and product quality. Here are some factors to consider when selecting equipment:
Material requirements: Different applications require different types of films. Understanding the characteristics of the target material will help you select the right equipment.
Deposition conditions: Deposition temperatures and pressure ranges need to be determined based on production needs to ensure that the equipment is capable of meeting specific process requirements.
Production scale: For large-scale production, choosing highly efficient CVD or PECVD equipment will help to increase yield and reduce production costs.
Brother Furnace: A Specialized Manufacturer of Thin Film Deposition Equipment
As a leading manufacturer in the field of thin film deposition, Brother Furnace is committed to providing high-performance CVD furnaces and PECVD
furnaces to meet the needs of different industries.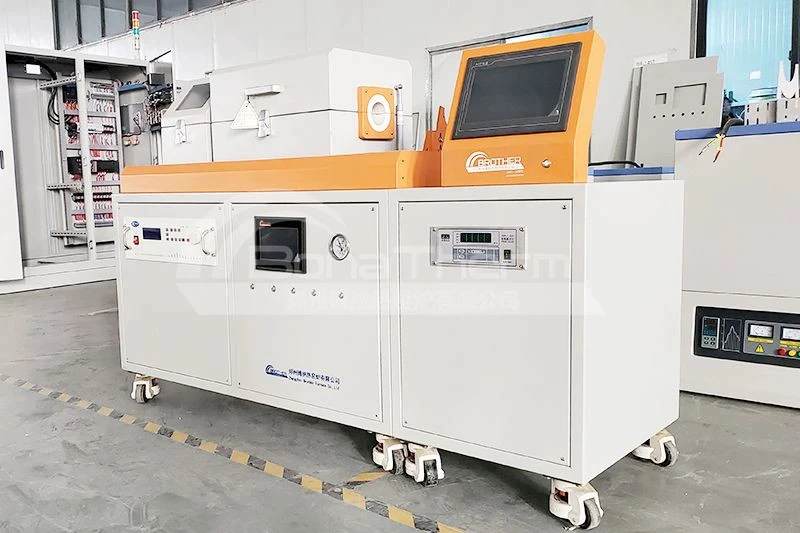
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) Furnaces
Feature: Brother Furnace's CVD furnaces feature an advanced design with an efficient gas distribution system to ensure uniform film thickness and high-quality deposition. The equipment supports a variety of gas precursors to adapt to the deposition needs of different materials.
Application example: In the semiconductor industry, our CVD furnaces are widely used to fabricate silicon-based thin films, providing customers with high-performance solutions.
Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) Furnaces
Feature: A PECVD furnace is suitable for the deposition of heat-sensitive materials by introducing plasma to increase the deposition rate and lower the deposition temperature. Brother Furnace's PECVD furnace features flexible gas input and precise process control to ensure excellent film performance.
Application example: In the photovoltaic industry, PECVD furnaces are used to manufacture thin films for high-efficiency solar cells, improving energy conversion efficiency.
Brother Furnace Looks Forward to Working with You!
Thin film deposition technology is an indispensable and important technology
in modern industry, which is widely used in many fields such as semiconductors,
photoelectricity, medicine and so on.
As a professional manufacturer of chemical vapor deposition furnaces, Brother Furnace is committed to providing customers with efficient and reliable thin film deposition solutions.
Brother Furnace believes that with the advancement of technology and the expansion of application areas, thin film deposition technology will bring innovation and breakthroughs to more industries.
If you are interested in thin film deposition technology or our vapor deposition furnace, please feel free to contact us.
