How to Choose a Tube Furnace?
Tube furnace is a heat treatment apparatus widely used in laboratories and industries, recognized for its distinctive design and remarkable performance. It finds applications in various processes like material synthesis, heat treatment, annealing, sintering, and chemical vapor deposition, meeting diverse heat treatment needs effectively. This guide delves into selecting an appropriate tube furnace to assist you in making an informed choice aligned with your requirements.
What is a Tube Furnace
Typically found in laboratories and industries, high-temperature tube furnaces offer advantages such as high-temperature capabilities, uniform heating, and atmosphere control. Consisting of a lengthy tubular furnace with external heating elements, they cater to processes like material synthesis, heat treatment, annealing, sintering, and chemical vapor deposition. Tube furnaces ensure precise temperature regulation and uniform heating under varied atmospheric conditions.
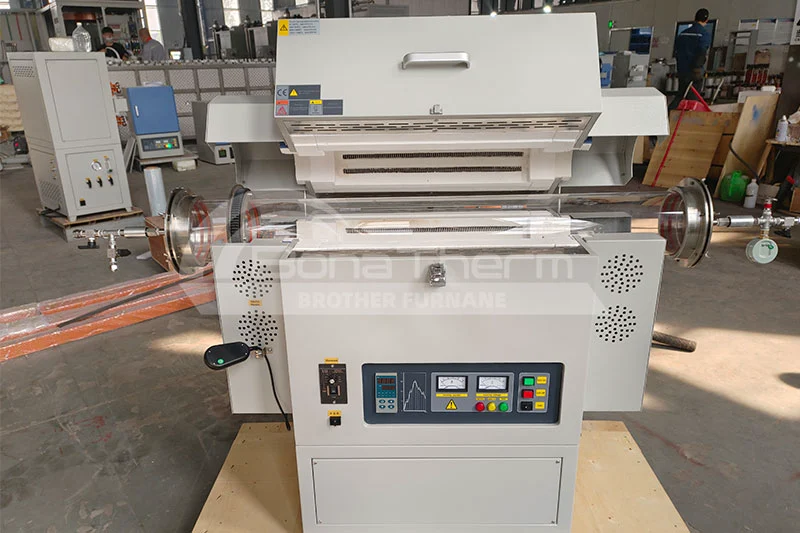

How to choose a suitable tube furnace?
Before choosing a tube furnace, we must first know whether we need a tube furnace. First, we must clarify the materials and corresponding processes that the tube furnace is commonly used to process to see if they match the materials and processes we want to process.
What materials can a tube furnace process?
The materials processed by the tube furnace include but are not limited to:
Metals: Materials like iron, copper, and aluminum are subjected to annealing, sintering, and heat treatment processes within the tube furnace.
Ceramics: such as alumina, silicon carbide, etc., are used for sintering and material synthesis.
Glass: Annealing and heat treatment of glass materials is facilitated by the tube furnace.
Composite materials: such as carbon fiber composites, are used for high-temperature heat treatment and synthesis.
 |  |
Different materials have different processing requirements at high temperatures. The versatility of the tube furnace enables it to adapt to the processing needs of a variety of materials. If you are unsure whether you are suitable for choosing a tube furnace, you can contact us and leave your information. In addition to tube furnaces, Brother Furnace also produces vacuum furnaces, muffle furnaces, debinding and sintering furnaces, atmosphere furnaces, and other equipment. We will recommend the most suitable equipment for you.
What to pay attention to before choosing a tube furnace
1. Determine your operating temperature range
Tube furnaces have a certain operating temperature range, usually from 1000℃-1800℃. Make sure your operating temperature is within the range that the tube furnace can support. Common ones include 1200℃ tube furnaces, 1300℃ tube furnaces, 1500℃ tube furnaces, etc.
2. Determine the size of the heating zone you need
First, please understand your sample size and processing requirements, and choose the appropriate heating zone length. The uniform temperature distribution is particularly important for long-term constant temperature treatment. Commonly used are 77mm tube furnaces.
3. Identify the required tube material
Select appropriate tube material according to the processing temperature and material, such as quartz tube furnace is suitable for high temperature and corrosive atmosphere, alumina tube furnace is suitable for ultra-high temperature processing, and stainless steel tube is suitable for low temperature and vacuum environment.
4. Heating and cooling rates
Consider whether your process requires rapid temperature increases or decreases. Some experiments require rapid temperature changes to control reaction rates.
5. Determine whether you need atmosphere control
Determine if an inert gas, reducing atmosphere, or vacuum environment is required. Certain processes such as sintering and chemical vapor deposition require specific atmosphere conditions.
6. Know your budget
Choose the tube furnace that best meets your needs within your budget. Balance cost and performance and choose the most cost-effective equipment. Different types and sizes of tube furnaces have different prices. Please contact us for detailed information.
The above points are some key points that need to be clarified when choosing a tube furnace. Of course, if you are not clear about your needs, you can contact us at any time and leave your questions. We will be happy to help you solve them.
Main types of Brother Furnace’s tube furnaces
Having gained insight into selecting a tube furnace, let's explore the various types of tube furnaces manufactured by Brother Furnace.
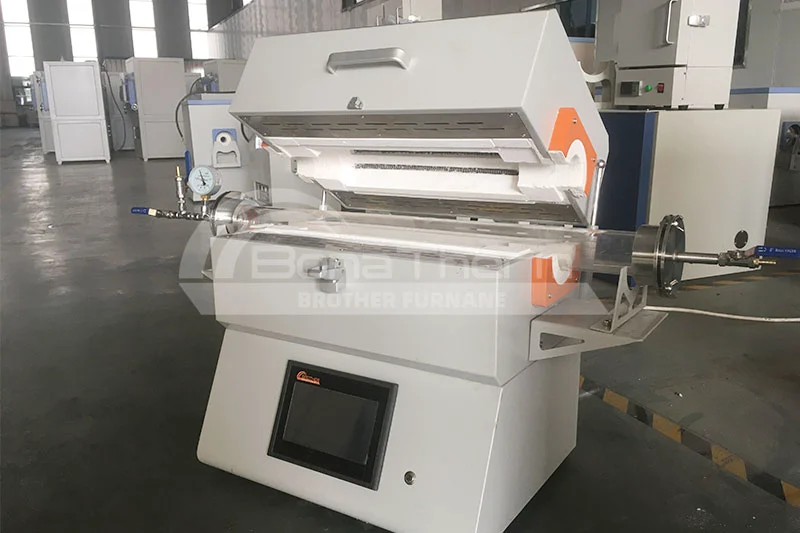 |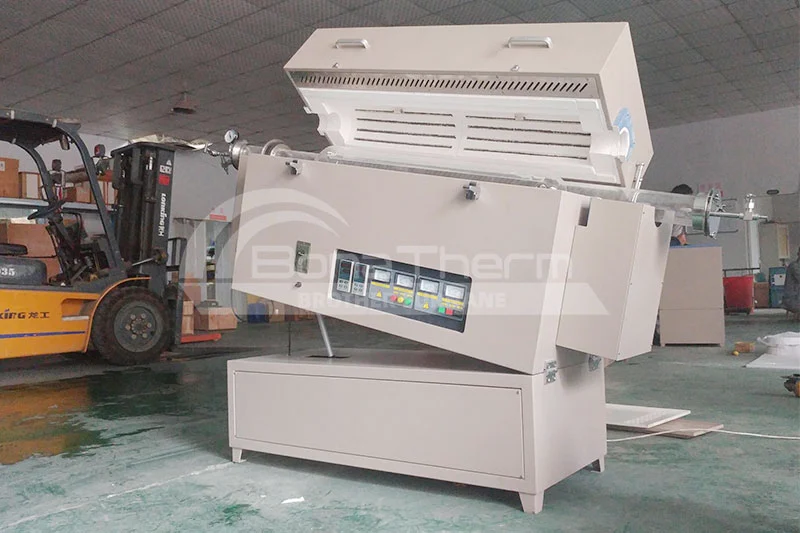  |  |
Operating temperature: 1200℃/1400℃/1600℃ Features: Easy to load and unload Even temperature distribution Application: Annealing, sintering, heat treatment | Operating temperature: 1200℃/1400℃/1600℃ Features: Tube rotation, uniform heating Application: Catalyst preparation, powder metallurgy, etc. | Operating temperature: 1200℃/1400℃/1600℃ Features: vertical placement, space-saving, suitable for long samples Applications: Materials testing, catalyst research, vertical evaporation |
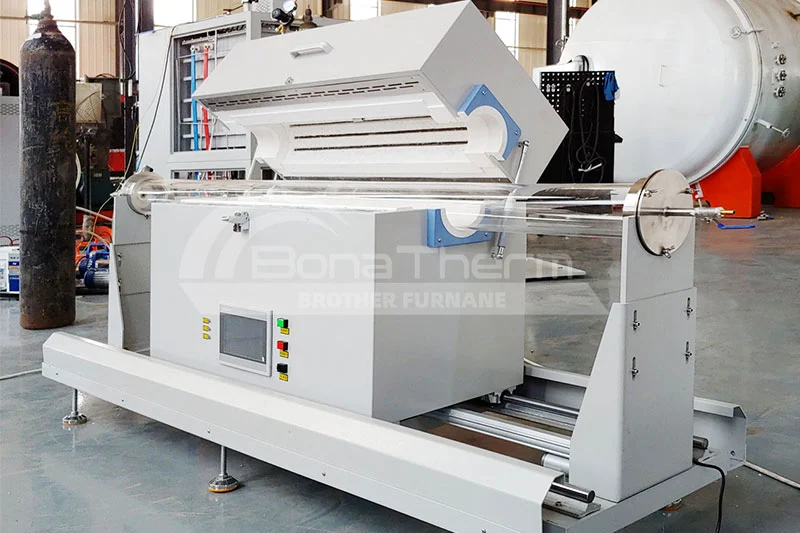 |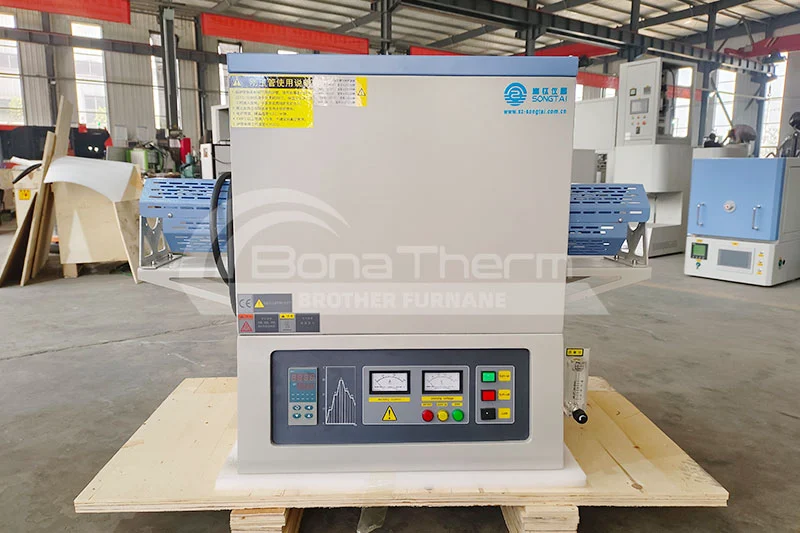  |
Sliding-type rapid cooling tube furnace Operating temperature: 1200℃/1400℃/1600℃ Features: Rapid cooling, sliding design, sudden temperature drop Application: rapid quenching, thermal shock test | Operating temperature: 1200℃/1400℃/1600℃ Features: vacuum environment, anti-oxidation, high-purity processing Applications: semiconductor manufacturing, precision ceramics, high-purity materials |
Summarize
Choosing the right tube furnace is crucial for effectively meeting the diverse heat treatment needs in laboratories and industries. Customize your tube furnace!
Brother Furnace offers a range of high-quality tube furnaces tailored to various applications, along with comprehensive pre-sales and after-sales support to ensure optimal performance and customer satisfaction. Explore our range of equipment to find the most suitable solution for your heat treatment processes.
